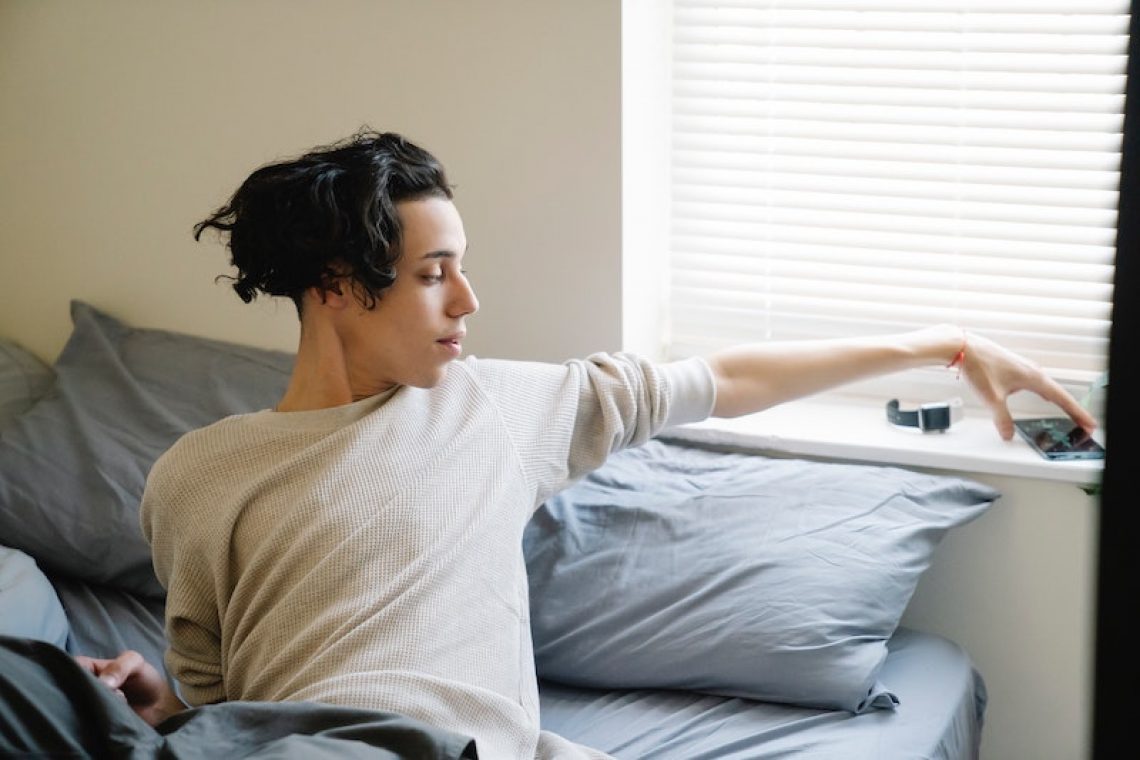
The juvenile justice system came about as a means of protecting our children. It isn’t meant to be this scary, punishment-focused thing that tries to scare the criminal behavior out of them. It doesn’t work and it certainly doesn’t lower recidivism rates.
On any given day in the United States, there are more than 50,000 people under the age of twenty-one in juvenile detention centers and many of these people will end up back in juvenile detention.
Continue reading to learn everything that you need to know about juvenile recidivism and how Steps for Change is working to reduce re-offenses amongst adolescents.
What Is Juvenile Recidivism?
Juvenile recidivism refers to the tendency of adolescent delinquents who:
- Commit a delinquent behavior
- Get taken into custody
- Adjudicated by the judge
- Taken to detention
- Get released
- Commit another delinquent behavior
Juvenile delinquents are more likely to commit another crime after their release from detention. In fact, within three years, 76% will end up back in detention. After five years, 80% will commit another crime and forty percent are likely to end up in adult prison by the time they turn 25.
There are certain factors in play when it comes to what youth are at risk to continue engaging in criminal behaviors.
What Causes These Higher Recidivism Rates?
Many factors lead to juveniles continuing to commit crimes. It boils down to:
- Who they meet while in detention
- Criminal records keeping them from finding (and then keeping) gainful employment
- Exacerbation of mental health issues
- Lack of support after detention
- Their living situation following detention
Children in detention may come into contact with drug dealers or hardened criminals who cause them to take on a more aggressive persona to make it through detention without becoming a victim.
Due to their time in a juvenile detention facility, it’s possible that they lost their job. And when they get out, they may have a record now that prevents them from finding a new job that will help them get their lives back on track.
Juveniles in the child welfare system are more likely to end up continuing their criminal behaviors. In fact, as many as two-thirds of these delinquents will re-offend. These children are lacking the necessary love and support needed to keep them out of trouble.
How Can We Lower the Rates?
There is an argument that juvenile’s who have committed crimes should:
- Focus on rehabilitation to grow as human beings
- Receive harsher consequences for their actions
Knowing that there are things that DO work and things that DON’T work is the first step toward lowering recidivism rates. Some things that don’t tend to work are:
- Retribution
- Incapacitation
- Deterrence
In fact, retribution and incapacitation are responsible for an 8% increase in recidivism. Deterrence is responsible for a 2% increase.
What’s done to correct these children could be considered as grounds for malpractice and abuse. And for what? It’s not working and it’s not helping to reduce the recidivism rates.
Fortunately, there are several different types of programs that do work to prevent juvenile recidivism, including:
- Restorative justice
- Parent training
- Drug treatment
- Behavior modification
- Cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT)
- Family, group, and multisystemic therapies
These program types all have an emphasis on rehabilitation. Juvenile’s need to have access to services that will help them get out of the criminal lifestyle. The Community Juvenile Accountability Act was created for rehabilitation and was responsible for a 24% drop in recidivism among juvenile delinquents.
Rehabilitation is a positive and progressive approach that shows juveniles and their families that they have access to the support needed to break the cycle and prevent criminal behavior relapse. It can intervene and modify those destructive behaviors.
Restorative Justice
Restorative justice helps to set youth on the right path after their criminal behaviors and detention has ended. In fact, restorative justice is responsible for a 38% reduction in recidivism. It acts as a mediator between the youth and the victim or community affected by their behaviors so that the youth can make amends for their behaviors.
Therapy for Delinquents
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy work well as a form of mental health treatment.
With CBT, it’s thought that there are errors in thinking patterns. This type of therapy allows the restructuring of these thought processes for the better. It helps juveniles to improve:
- Social skills
- Problem-solving
- Critical reasoning
- Moral reasoning
- Self-control/ impulse management
- Self-efficacy
Family therapy focuses on reducing negativity within the familial structures. It teaches parents and family members essential skills like communication, efficient parenting, and conflict management.
Treatment Programs
Many juvenile’s struggle with some sort of issue that they will need treatment for as a part of their rehabilitation back into society. There are treatment programs available to those struggling with drug and alcohol use. If they happen to be struggling with mental health problems (such as sexual behavior problems), there is also help available for them.
Don’t Wait to Get Help
Juvenile recidivism is a huge problem among teenagers who have served time in a juvenile detention facility for partaking in criminal behavior. If you know a youth who is struggling to get their life back on track after spending time in a juvenile detention facility, you can help.
At Steps for Change, we offer Counseling & Psychotherapy Services to help rehabilitate youth and get them set in the right direction for the rest of their lives. At Steps For Change, we specialize in treating children and adolescents with problems involving mental health and sexual behaviors.
Contact us today for more information on how we can help lower recidivism rates amongst adolescent criminal behavior.